
Obesity has grown to be a significant health issue in today’s society, since it plays a role in the development of chronic illnesses like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Customized food plans for weight loss have become more common as a result. The ketogenic diet, sometimes referred to as the “keto diet,” is one such program. The high-fat, low-carb keto diet seeks to promote weight loss, improve mental clarity, and increase energy levels. The ketogenic diet will be thoroughly explained in this post, along with its advantages, disadvantages, and important points.
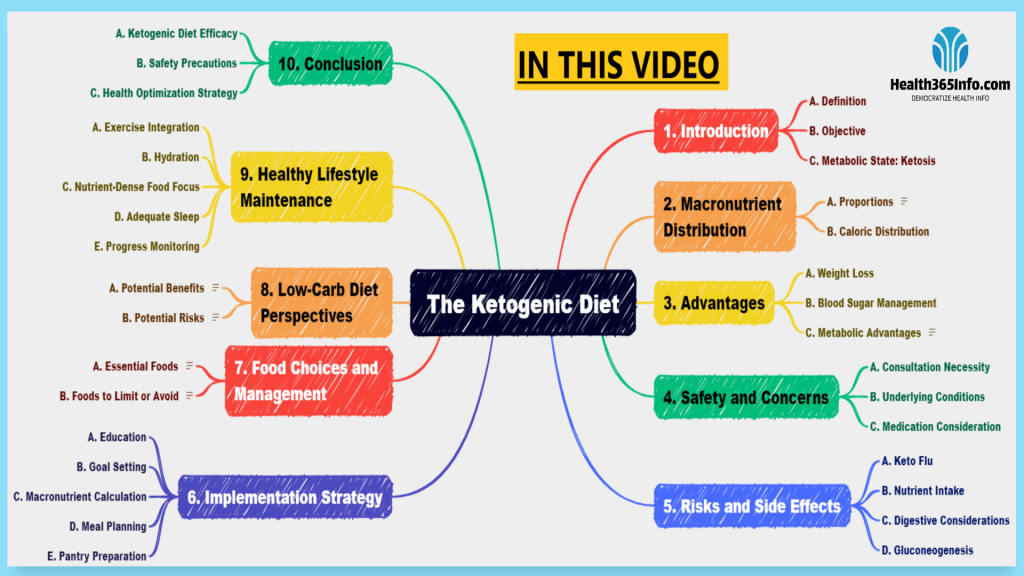
Knowledge of the Ketogenic Diet
The Ketogenic Diet: What Is It?
Intake of high-fat and low-carbohydrate foods is a hallmark of the ketogenic diet. This diet causes the body to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis, when fat is used as the body’s primary fuel source rather than carbs. This metabolic state is brought about by dramatically reducing carbohydrate intake while boosting fat and protein intake. The ketogenic diet’s main objectives are to reduce total body fat and enhance metabolic health.
The Ketogenic Diet: How Does It Operate?
The body enters a nutritional ketosis condition when carbs are reduced. The liver creates ketones from fat in this condition, which the body uses as an additional energy source. The breakdown of fatty acids results in the production of ketones, which give the brain and muscles a constant supply of energy.
Distribution of Macronutrients in the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet often entails consuming large amounts of fat, a moderate amount of protein, and little or no carbohydrates. Depending on personal needs and objectives, the precise ratios may change, but a typical distribution is roughly 70–75% of calories from fat, 20–25% from protein, and 5–10% from carbohydrates.
Advantages of a Ketogenic Diet
Loss of weight
Weight loss is one of the main reasons individuals choose the ketogenic diet. The diet’s low-carb and high-fat composition might cause quick weight reduction, especially in the beginning. This is due to the fact that in the lack of carbs, the body is compelled to utilise stored fat as fuel.
Blood Sugar Management
The ketogenic diet has demonstrated promise in terms of enhancing blood sugar regulation, particularly in people with type 2 diabetes. The diet helps control blood sugar levels by limiting carbohydrate intake, which may lessen the need for diabetes medication.
Metabolic Advantages
There may be various metabolic advantages to the ketogenic diet, according to research. It can lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), also referred to as “bad” cholesterol, and raise levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), also referred to as “good” cholesterol. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the diet lowers triglyceride levels, which are linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
Considerations for Safety
Although the ketogenic diet has demonstrated promising benefits for weight loss and enhanced metabolic health, safety issues must be taken into account. It is advised to speak with a healthcare provider before beginning the diet if you have any underlying medical conditions or are on medication because it may not be appropriate for everyone.
Risks and Potential Adverse Reactions
Symptoms of Ketosis
The “keto flu” is a condition that some people may have while switching to a ketogenic diet. This is a brief collection of symptoms that can include irritability, headaches, nausea, and exhaustion. As the body adjusts to using ketones as fuel, these symptoms typically go away within a few days to a week.
dietary considerations
Since the ketogenic diet limits carbohydrate intake, it’s crucial to make sure you’re getting enough of the nutrients you need. By emphasizing nutrient-dense meals and include a variety of veggies, healthy fats, and lean proteins in the diet, this can be accomplished.
Gluconeogenesis
The body’s capacity to create glucose from sources other than carbohydrates is known as gluconeogenesis, and it should be taken into account when following a ketogenic diet. Despite the fact that the body can make glucose from proteins, this process is often under tight control and does not significantly endanger general health.
Health Resources and Assistance
It is crucial to get advice and information on the ketogenic diet from reputable medical sources before starting. A registered dietitian or other healthcare professional with expertise in the ketogenic diet can offer you individualized guidance and support all along the way.
Adopting a ketogenic diet
Introduction to the Ketogenic Diet
If you’re thinking about starting a ketogenic diet, it’s crucial to organize and get ready for the change. To get you started, follow these steps:
Educate Yourself: Get to know the tenets and regulations of the ketogenic diet to know how it operates and what to anticipate.
Determine your health or weight loss goals, and create a plan to monitor your progress.
Calculate Macronutrient Ratios: To find the proper macronutrient ratios for your unique needs, use internet calculators or speak with a dietitian.
Plan Your Meals: Make a meal plan that complies with the macronutrient ratios recommended by the ketogenic diet and incorporates a variety of foods that are high in nutrients.
Stock Your Pantry: Get rid of high-carbohydrate items and stock up on keto-friendly products like lean proteins, low-carb vegetables, and healthy fats.
Food Options and Carb Counts
Making thoughtful food selections and paying attention to carbohydrate amounts are crucial when following the ketogenic diet. Following are some illustrations of meals to include and avoid:
Suitable Foods:
Avocado, olive oil, and coconut oil are examples of healthy fats.
sources of protein such meat, poultry, fish, and eggs
Non-starchy vegetables include broccoli, cauliflower, and leafy greens
seeds and nuts
dairy items with added fat, such as cheese and yogurt
Limit Your Eating:
Starchy vegetables, legumes, and grains are examples of high-carbohydrate foods.
Added sugars in foods and drinks
processed foods and snacks
Benefits and Risks of Low-Carbohydrate Diets
Although the ketogenic diet has been linked to a number of health advantages, it’s crucial to recognize that low-carb diets might not be right for everyone. The following are some possible advantages and hazards of low-carb diets:
Benefits:
Loss of weight
improved control over blood sugar
decreased risk of some diseases
an increase in energy
Risks:
Lack of nutrients if not properly planned for
Possible elevation of LDL cholesterol levels
difficulty maintaining the diet over the long term
Upholding a Healthful Lifestyle
In spite of the fact that the ketogenic diet may be a useful tool for weight loss and better metabolic health, it’s crucial to maintain a healthy, sustainable lifestyle. The following advice will help you live a healthy lifestyle while on the ketogenic diet:
Keep Moving: Include frequent exercise in your routine to enhance your general health and wellbeing.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to support your body’s numerous processes.
Focus on entire Foods: To make sure you’re getting a variety of critical nutrients, choose entire, nutrient-dense foods.
Prioritize Sleep: To maintain general health and maximize the advantages of the ketogenic diet, strive for adequate sleep.
Monitor Your Progress: Keep tabs on your development and adjust as necessary to make sure you’re accomplishing your objectives.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet is a very powerful strategy for losing weight and enhancing metabolic health. The body reaches a state of ketosis, where it uses fat as its main fuel source, by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and considerably boosting fat and protein intake. Prior to beginning the diet, it is crucial to take safety precautions, examine any adverse effects, and speak with a healthcare provider. People who follow the ketogenic diet in a well-thought-out and well-balanced way may experience weight loss, better blood sugar regulation, and metabolic advantages. To maximize long-term success while consuming foods that promote a ketogenic lifestyle, keep these in mind.
KEY References
Ludwig, D. S. (2020, June 1). The Ketogenic Diet: Evidence for Optimism but High-Quality Research Needed. Journal of Nutrition; Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxz308
Westman, E., Tondt, J., Maguire, E., & Yancy, W. S. (2018, September 3). Implementing a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism; Taylor & Francis. https://doi.org/10.1080/17446651.2018.1523713
Paoli, A. (2014, February 19). Ketogenic Diet for Obesity: Friend or Foe? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110202092
Bostock, E. C. S., Kirkby, K. C., Taylor, B., & Hawrelak, J. (2020, March 13). Consumer Reports of “Keto Flu” Associated With the Ketogenic Diet. Frontiers in Nutrition; Frontiers Media. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00020
Insulin Resistance. (2023, January 1). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29939616/
Masood, W. (2023, June 16). Ketogenic Diet. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/
Benton, D., & Young, H. (2017, June 28). Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight. Perspectives on Psychological Science; SAGE Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691617690878
Hall, K. D., Chen, K. Y., Guo, J., Lam, Y. Y., Leibel, R. L., Mayer, L., Reitman, M. L., Rosenbaum, M., Smith, S. R., Walsh, B. T., & Ravussin, R. (2016, July 6). Energy expenditure and body composition changes after an isocaloric ketogenic diet in overweight and obese men. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition; Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.133561
Sumithran, P., Prendergast, L. A., Delbridge, E., Purcell, K., Shulkes, A., Kriketos, A. D., & Proietto, J. (2013, May 1). Ketosis and appetite-mediating nutrients and hormones after weight loss. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition; Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.90
Melkonian, E. A. (2023, May 1). Physiology, Gluconeogenesis. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541119/
Deemer, S. E., Plaisance, E. P., & Martins, C. (2020, May 1). Impact of ketosis on appetite regulation—a review. Nutrition Research; Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2020.02.010
Paoli, A., Bosco, G., Camporesi, E. M., & Mangar, D. (2015, February 2). Ketosis, ketogenic diet and food intake control: a complex relationship. Frontiers in Psychology; Frontiers Media. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00027
Joshi, S., & Mohan, V. (2018, January 1). Ketogenic diets: Boon or bane? Indian Journal of Medical Research; Medknow. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_1666_18
Leidy, H. J., Clifton, P., Astrup, A., Wycherley, T. P., Westerterp-Plantenga, M. S., Luscombe-Marsh, N. D., Woods, S. C., & Mattes, R. D. (2015, April 29). The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition; Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.114.084038
Dyson, P., Beatty, S., & Matthews, D. R. (2007, December 1). A low-carbohydrate diet is more effective in reducing body weight than healthy eating in both diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabetic Medicine; Wiley-Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02290.x
Ketogenic Diet. (2023, January 1). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763005/
Sinha, S., & Kossoff, E. H. (2005, May 1). The Ketogenic Diet. The Neurologist; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nrl.0000160818.58821.d2
O’Neill, B. J., & Raggi, P. (2020, January 1). The ketogenic diet: Pros and cons. Atherosclerosis; Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.11.021













